Diabetes is a complex metabolic disease affecting how your body uses sugar from food for energy. Diabetes can have a range of health implications and impact the eyes.
A diabetic eye exam is more than just a routine health check; it’s part of diabetes management to help detect a spectrum of eye health challenges that can potentially be triggered by diabetes. Regular eye exams are a defense against diabetic eye diseases that can threaten your vision.
Diabetes & Your Body
Diabetes occurs when your body can’t produce enough insulin or use the insulin the body produces effectively. Insulin is a hormone that regulates the amount of sugar in the blood.
When the body struggles to produce or respond to insulin properly, it leads to abnormal blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar can damage the organs and nerves in the body.
Risk factors for developing diabetes can include:
- Insulin Resistance
- Poor dietary choices
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Family history of diabetes
- Age
Diabetes & Your Eyes
High blood sugar levels can also damage the blood vessels in the eye, particularly the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Damage can cause symptoms such as blind spots and blurred vision.
Without treatment, diabetes can increase your risk of developing a range of eye diseases, including:
- Diabetic retinopathy: This is one of the leading causes of blindness in Canada and results from swelling and bleeding blood vessels and abnormal blood vessel growth in the eye from high blood sugar.
- Diabetic macular edema: Leaking blood vessels cause fluid buildup in the macular or central part of the retina responsible for central vision.
Diabetic eye diseases can often develop slowly over time and without noticeable changes to your vision, making regular exams crucial for early detection and successful treatment.
What Is a Diabetic Eye Exam?
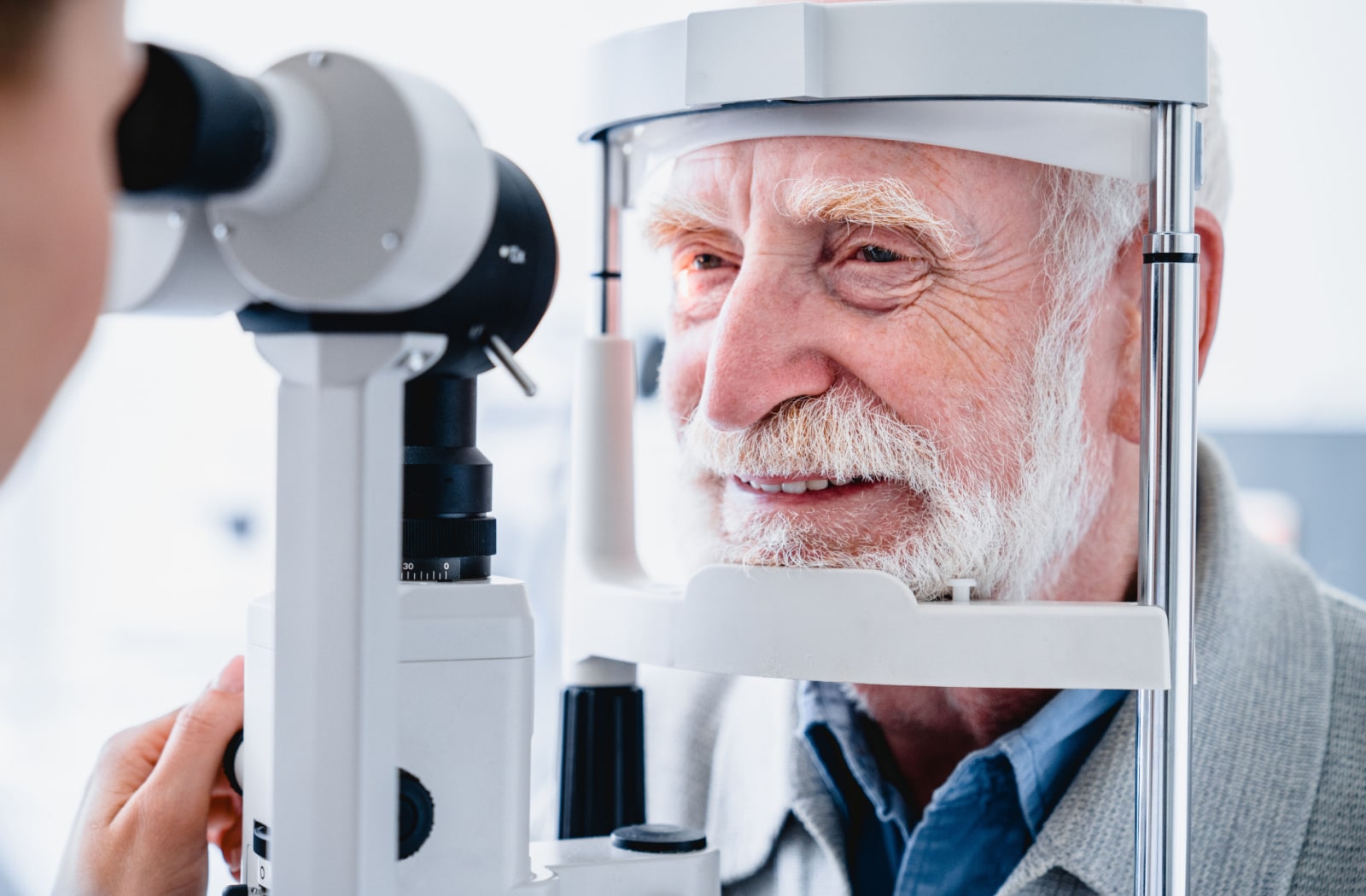
A diabetic eye exam performed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist includes dilating the pupils to examine the retina and signs of diabetic eye diseases. Sometimes, an eye exam can detect signs of diabetes before a diagnosis by your healthcare provider. At Orchard Park Optometry we also include Optomap Widefield Retinal Imaging to check for diabetic retinopathy, and an OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) of the macula to check for Diabetic Macular Edema.
An eye exam could potentially save your sight, offering timely intervention for visual complications arising from diabetes and should be a non-negotiable part of your healthcare routine for several reasons.
Early Detection Equals Early Prevention
Many diabetic eye diseases progress without immediately visible symptoms, and so early detection through a diabetic eye exam is invaluable. It allows for early intervention, preventing or slowing the progression of sight-threatening conditions.
Protection Against Vision Loss
Identifying potential problems early with a diabetic eye exam can prompt necessary action and treatment. Managing prediabetes without medication can include engaging in physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating a healthy diet. Managing diabetes can involve monitoring and regulating blood sugar with medication.
Monitoring Retinopathy
The primary goal of diabetic eye exams is to monitor for diabetic retinopathy, the leading cause of blindness in working-age adults. Regular assessments note any changes in the eye for appropriate management.
What Happens in a Diabetic Eye Exam?
The thought of a new medical procedure can be intimidating, but understanding what’s involved in a diabetic eye exam can alleviate any anxiety. Standard procedures or tests performed during a diabetic eye exam can include the following:
- Dilation: This involves using eye drops to dilate the pupil or make them larger, allowing your eye doctor to examine the retina and the back of the eye.
- Retinal imaging: Imaging technologies such as Optomap imaging provide a detailed view of the eye’s inner workings and the vascular system around the retina.
Frequency of Diabetic Eye Exams
Adults between 20 and 64 should have a comprehensive eye exam at least every 2 years or more frequently if recommended by your eye doctor. However, if you have diabetes, you should have a diabetic eye exam at least once a year. With diabetes, you’re at an increased risk of diabetic eye diseases, and with age, you’re at an increased risk of developing eye diseases such as glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, and cataracts.
How to Reduce Your Risk of Diabetic Eye Diseases
Diabetic eye exams work with overall diabetes management strategies as a comprehensive approach to care. By managing your diabetes, you also manage some of the risks associated with it:
- Monitor blood sugar levels
- Monitor blood pressure levels
- Monitor cholesterol levels
- Exercise, eat healthy, and maintain healthy body weight
- Stop smoking
Follow Up with Your Optometrist
Regular eye exams are imperative for individuals living with diabetes to prevent potential complications that could lead to vision loss.If you have diabetes or are at risk, your eyes and your overall health deserve the attention and care that only a professional diabetic eye exam can provide. Book an appointment with Orchard Park Optometry today.